In the fastener mold industry, understanding the different types of metal fasteners molds is crucial for manufacturers and end-users alike. Metal fasteners are essential components in various industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery. This comprehensive guide will explore the key types of metal fasteners molds, their design considerations, manufacturing processes, and how to select the right mold for your specific application.
Metal Fasteners Molds
Metal fasteners molds are specialized tools used to manufacture bolts, studs, screws, nuts, and dies with high precision. These molds are designed to withstand the rigorous demands of high-volume production and to ensure the consistent quality of each fastener produced. Given the critical role that fasteners play in securing structural integrity and performance in assemblies, the molds used in their production must be engineered to exact specifications and high standards.
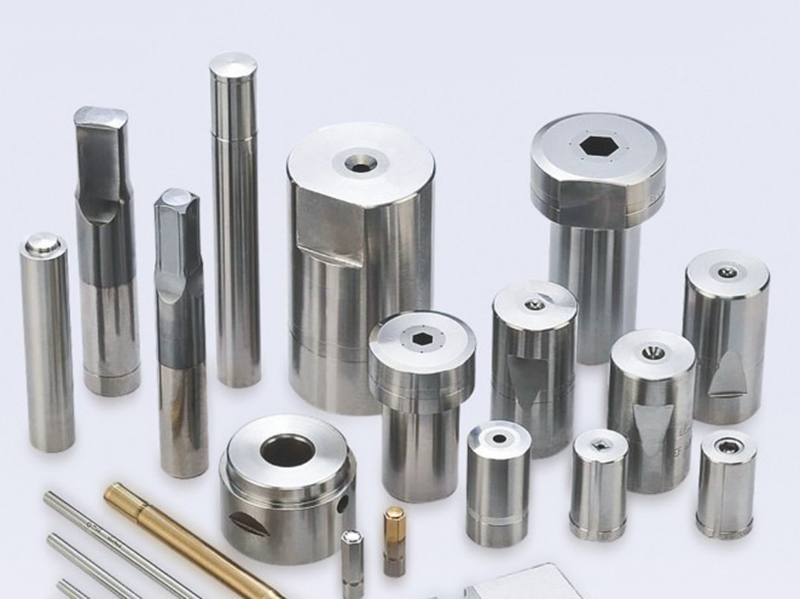

Key Components of Metal Fasteners Molds
Before diving into the different types of metal fasteners molds, it’s important to understand the core components that make up these molds:
Cavity and Core Inserts: These parts form the shape of the fastener. The cavity creates the external features while the core insert forms the internal features.
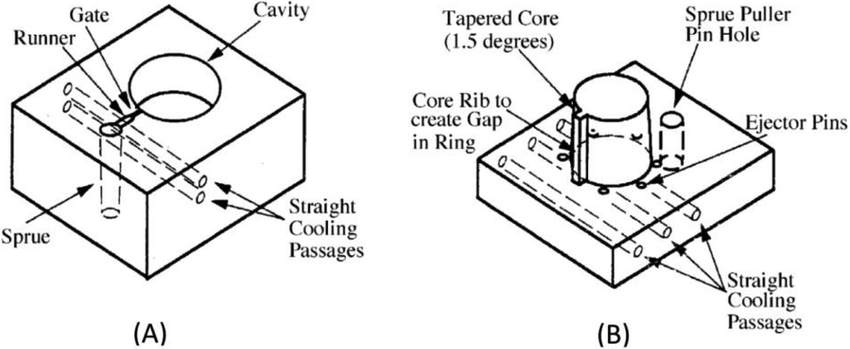
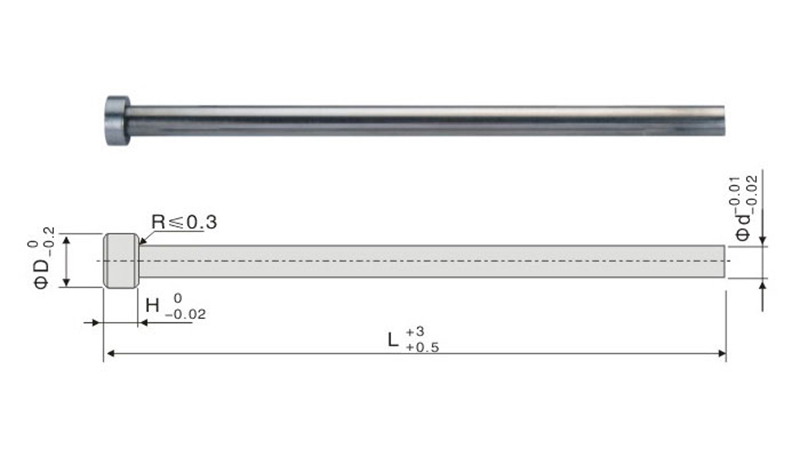
Ejector Pins: These components are used to remove the fastener from the mold after the casting or forging process.
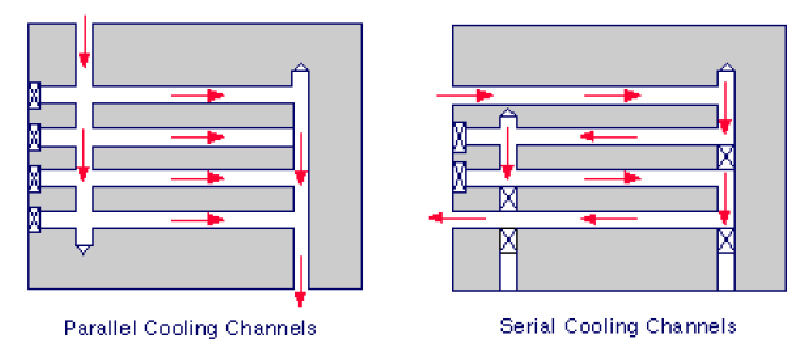
Cooling Channels: Efficient cooling channels are integrated into the mold design to maintain temperature control during production, ensuring the metal fasteners set properly.
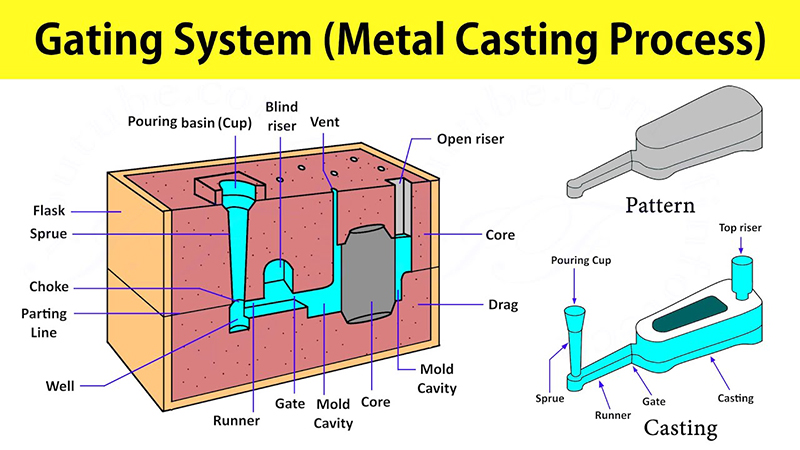
Sprue and Gate Systems: These systems control the flow of metal into the mold, ensuring even distribution and reducing the risk of defects.
Understanding these components is essential when selecting or designing a mold for metal fasteners.
Types of Metal Fasteners Molds
There are several types of metal fasteners molds available, each with unique characteristics and applications. Below, we examine the most common types.
1. Cold Heading Molds
Cold heading molds are widely used in the production of screws, bolts, and other small fasteners. In this process, metal wire is fed into the mold, where it is cut and formed at room temperature using high-speed mechanical presses. This method is highly efficient and offers several advantages:
High Production Rates: The process is suitable for high-volume manufacturing.
Material Efficiency: Minimal waste is produced during the molding process.
Precision and Consistency: Cold heading molds provide excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
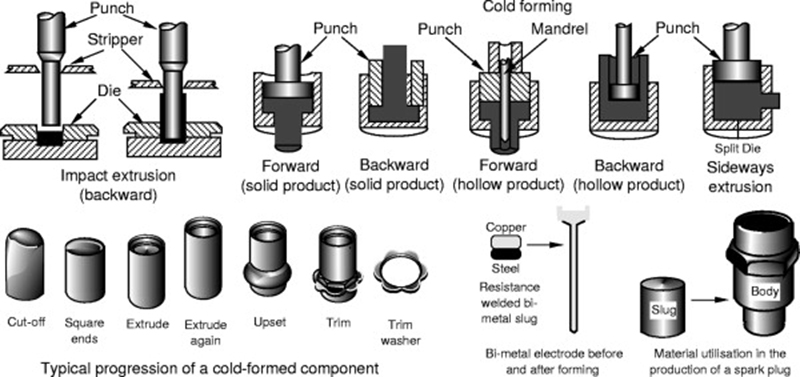
These molds are typically used for creating parts with simple geometries. Their precision and efficiency make them an excellent choice for standard fastener production.
2. Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds are used for fasteners that require complex shapes or that benefit from the properties of cast metals. In the die casting process, molten metal is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. This technique is especially useful for fasteners that need to combine strength with intricate designs:
High Dimensional Accuracy: Die casting provides close tolerances, which are critical for fasteners.
Surface Finish: Parts produced by die casting often require minimal post-processing.
Complex Geometries: The process allows for the creation of intricate designs that would be difficult to achieve with other molding methods.
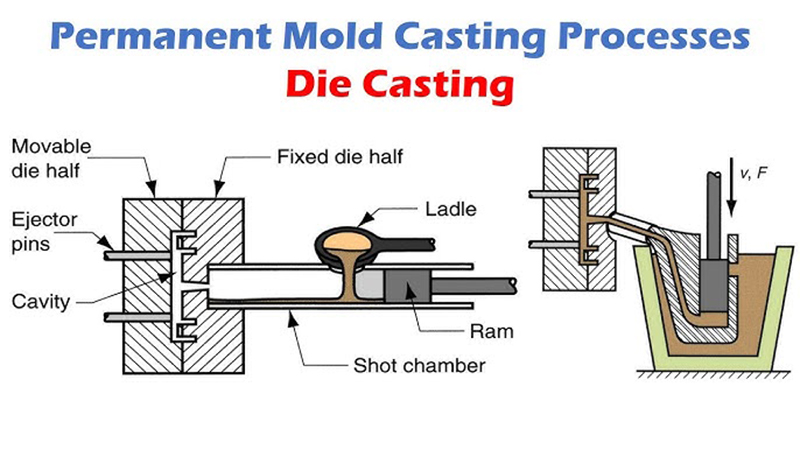
Die casting molds are favored in industries where precision and complex design features are paramount.
3. Hot Forging Molds
Hot forging molds are used in the production of large or high-strength fasteners. This process involves heating the metal to a high temperature and then forming it in a mold under significant pressure. The advantages of hot forging include:
Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The process results in a fine-grained microstructure, improving strength and durability.
Versatility: Hot forging is suitable for a wide range of metals, including high-strength alloys.
Improved Fatigue Resistance: Forged fasteners typically have better fatigue resistance compared to those produced by casting.
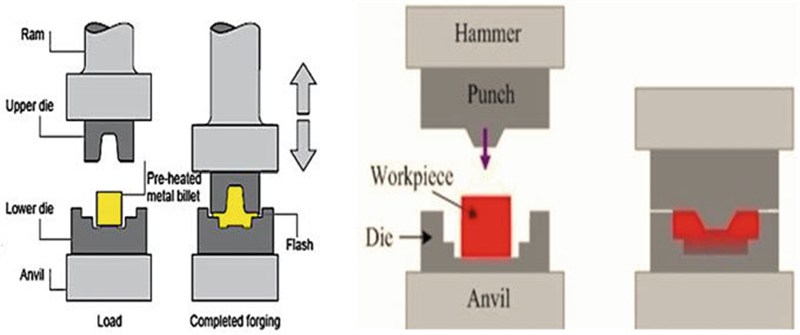
Due to the high pressures and temperatures involved, hot forging molds must be constructed from high-performance materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions.
4. Powder Metallurgy Molds
Powder metallurgy molds are used in the production of fasteners that require specific material properties, such as high wear resistance or unique mechanical characteristics. The process begins with metal powders that are compacted in a mold and then sintered at high temperatures. Key benefits include:
Material Efficiency: Powder metallurgy allows for precise control over the composition and distribution of materials.
Complex Shapes: This method enables the production of parts with complex geometries that would be difficult to machine or forge.
Cost-Effective for High-Volume Production: Once the mold is designed and manufactured, powder metallurgy can be highly economical.
This method is often used for fasteners that need to meet stringent performance criteria or where weight reduction is a key consideration.
5. Investment Casting Molds
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a process used for creating high-precision, intricate fasteners. A wax pattern is created and then coated with a refractory material to form a mold. Once the mold is heated and the wax is removed, molten metal is poured into the cavity. The process offers several benefits:
High Detail and Accuracy: Investment casting is capable of producing parts with very fine details and complex shapes.
Smooth Surface Finish: The parts produced typically require minimal post-casting finishing.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals, including exotic alloys.
Investment casting molds are ideal for applications where the aesthetic finish and high accuracy of the fastener are important.
Design Considerations for Metal Fasteners Molds
When designing or selecting a mold for metal fasteners, several key factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and product quality:
Material Selection
Choosing the right mold material is critical. High-performance tool steels are commonly used due to their durability, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The material must be compatible with the metal being cast, forged, or pressed.
Mold Durability and Maintenance
The production environment in the fastener industry can be harsh. Molds must be designed for longevity and ease of maintenance. Incorporating features such as replaceable inserts and optimized cooling systems can help extend the mold's life and reduce downtime.
Tolerance and Precision
Metal fasteners often need to meet strict dimensional tolerances. The mold design should allow for high precision in the final product. This is particularly important in applications where even minor deviations can compromise the integrity of the assembly.
Cost Considerations
While high-quality molds might involve a significant initial investment, the long-term benefits in terms of production efficiency, reduced waste, and fewer defects can lead to substantial cost savings over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership is crucial when selecting the appropriate mold type.
Future Trends in Metal Fasteners Molds
The fastener mold industry is continually evolving with advancements in manufacturing technology. Some emerging trends include:
Automation and Robotics: Increased use of automation in the molding process is leading to higher production rates and improved consistency.
Advanced Materials: The development of new alloy compositions and composite materials is enhancing mold durability and performance.
Digital Simulation: Computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation software are being used to optimize mold designs before production, reducing the need for costly trial-and-error iterations.
Sustainability Initiatives: Manufacturers are increasingly focused on reducing waste and energy consumption, with innovations in mold design contributing to more sustainable production practices.
Conclusion
Understanding the Types of metal fasteners molds is essential for anyone involved in the fastener manufacturing industry. Whether you are working with cold heading, die casting, hot forging, powder metallurgy, or investment casting, each mold type offers unique advantages tailored to specific production needs. By carefully considering design factors such as material selection, durability, precision, and cost, manufacturers can optimize their production processes, enhance product quality, and remain competitive in a dynamic market.
As the industry continues to innovate with advanced materials and digital design tools, staying informed about the latest trends and technologies will be crucial. Manufacturers who invest in high-quality molds and adopt modern manufacturing techniques will be well-positioned to meet the increasing demands of various industrial applications.
In summary, the selection of the appropriate mold type—whether it’s for creating standard bolts or intricate fasteners with specific performance requirements—plays a pivotal role in the overall success of the manufacturing process. With a focus on precision engineering and continual improvement, the fastener mold industry will continue to evolve, delivering products that are integral to the performance and safety of modern machinery and structures.
By mastering the intricacies of Types of metal fasteners molds, you can ensure that your production processes are not only efficient but also produce high-quality fasteners that meet the rigorous demands of today's engineering challenges.
